DNS Management explanation
Using DNS ensures that your website and email are accessible on the internet.
Nowadays that is no longer the only thing you do with DNS. DNS is similar to a phone book.
In your DNS you indicate where a particular service runs and how it should get there.
For example, you can think of mail services that are used externally, such as:
- Gmail
- Office365
- Spam filters
- But other external services also use your DNS.
It is therefore very important to create the DNS records correctly.
When creating/adding a record you can indicate the type of record:
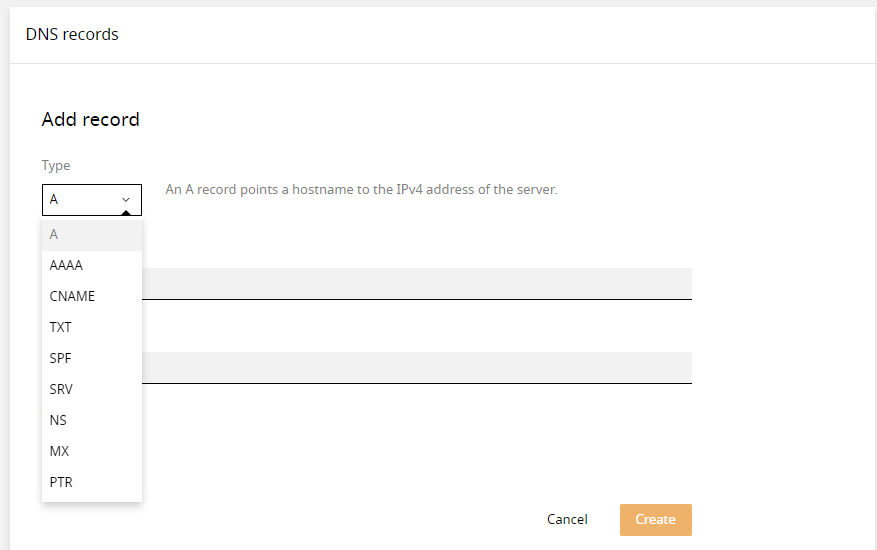
- An A record always refers to an IPv4 address.
- An AAAA record always refers to an IPv6 address.
- For example, a CNAME record is used for a subdomain
- A TXT record is usually for SPF, DKIM and DMARC records. A TXT record is also used by Microsoft to validate domain ownership
- An SPF record is no longer used, this is the predecessor of TXT.
- An SRV record is no longer used
- An NS record is used to announce Namesrevers
- An MX record is used to indicate where email should be delivered
- A PTR record is used to validate a reverse DNS.
A number of basic steps that must be taken into account when creating and modifying DNS records are:
- A CNAME record target field to external locations must always end with a .
- An MX record and then the target field must always end with a .
- With a CNAME / TXT record, the host field must be filled with an @ unless a subdomain is referred to.
Thank you for your feedback.
Sorry about that :( We'll work to make it better.
You voted before.
(114 times viewed / 1 people found it helpful)
